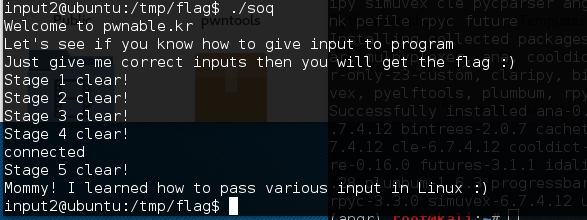
感觉PWN是真的好玩又磨人。。。
怀念re那种单纯的日子。。。
* 值得记录的地方
wp网上到处都是,我也是看别人的学会解题的。所以就在这里记录一些我新学的姿势
1.可以利用管道通信重定向read(0)和read(2)(也就是标准输入和标准错误
2.自己写的代码只能存到tmp文件夹下(通过scp命令也可以自己拖进去)
3.最好在tmp文件夹下新建一个文件夹,这样可以用ls查看自己拖进去的东西
4.由于题目程序cat flag是在input文件夹,所以要用软连接ln -s /home/input2/flag /tmp/自己的文件夹名把那边输出的内容链接过来
* 解题脚本
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
int main()
{
char* argv[101] = { "home/input2/input",[1 ... 99] = "B",NULL };
argv['A'] = "\x00";
argv['B'] = "\x20\x0a\x0d";
argv['C'] = "9999";
int pipe2stdin[2] = { -1,-1 };
int pipe2stderr[2] = { -1,-1 };
pid_t childpip;
if (pipe(pipe2stdin) < 0 || pipe(pipe2stderr) < 0) {
perror("pipe error!");
exit(1);
}
FILE * fp = fopen("\x0a", "w");
fwrite("\x00\x00\x00\x00", 4, 1, fp);
fclose(fp);
if ((childpip = fork()) < 0) {
perror("fork error!");
exit(1);
}
if (childpip == 0) {
close(pipe2stdin[0]);close(pipe2stderr[0]);
write(pipe2stdin[1], "\x00\x0a\x00\xff", 4);
write(pipe2stderr[1], "\x00\x0a\x02\xff", 4);
}
else {
close(pipe2stdin[1]);close(pipe2stderr[1]);
dup2(pipe2stdin[0], 0);dup2(pipe2stderr[0], 2);
close(pipe2stdin[0]);close(pipe2stderr[0]);
char *envp[2] = { "\xde\xad\xbe\xef=\xca\xfe\xba\xbe",NULL };
execve("/home/input2/input", argv, envp);
perror("exe error!");
exit(1);
}
sleep(5);
int sockfd;
struct sockaddr_in server;
sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (sockfd < 0) {
perror("socket error!");
exit(1);
}
server.sin_family = AF_INET;
server.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("127.0.0.1");
server.sin_port = htons(9999);
if (connect(sockfd, (struct sockaddr*)&server, sizeof(server))) {
perror("connect error!");
exit(1);
}
printf("connected\n");
char buf[4] = "\xde\xad\xbe\xef";
write(sockfd, buf, 4);
close(sockfd);
return 0;
}
|
* 结果